Tokenomics
This page describes the basic parameters of Bridgeless tokenomics and changes that have been done in the existing CosmosSDK modules (e.g. staking, distribution, mint).
- Limit tokens emission to 1000000000 (1B) BRIDGE and additionally each token has 18
decimals (the underling token denom is
abridge). - All tokens are split to 3 pools and managed by accumulator module.
- Rewards by a block can be taken only from the accumulator module.
- System operates a new NFT module. The NFT module holds locked native tokens that can be delegated, undelegated, etc.
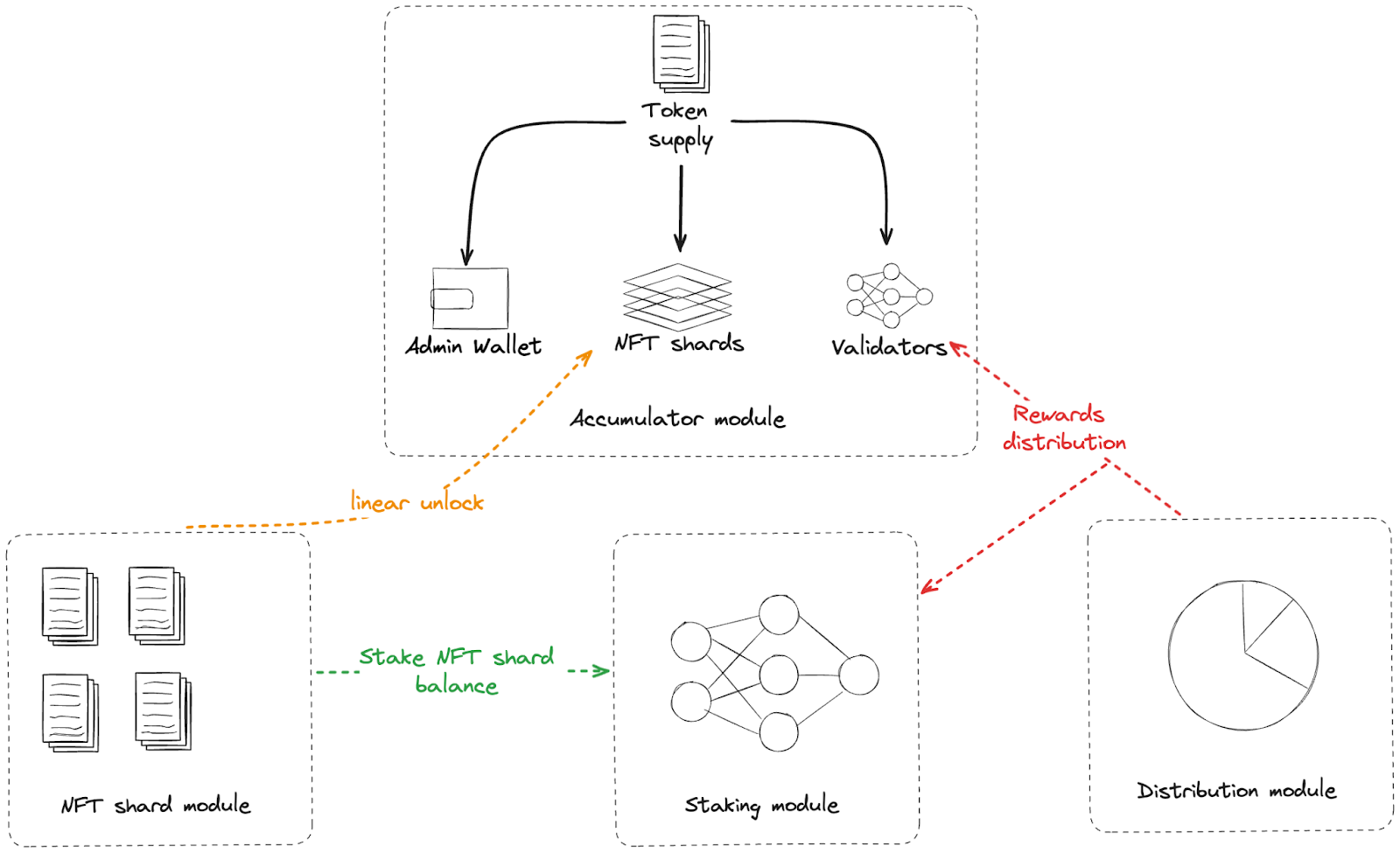
Involved modules
Staking
The enhanced CosmosSDK staking module extends the existing functionality of delegations, undelegations, redelegations, and voting power within a Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) system. This extension introduces support for custom non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that represent locked native tokens, ensuring seamless integration with the existing staking and governance mechanics.
Key Features and Functionality
- NFT-Based Delegation Support
- The module now supports delegation using custom NFTs.
- Each NFT represents a specific amount of locked native tokens, integrated into the staking ecosystem.
- Delegated NFTs provide the same functionality and benefits as standard token-based delegations.
- Voting Power
- Tokens delegated via NFTs contribute to the validator's voting power in the same manner as standard delegations.
- Delegators using NFTs maintain full governance rights, allowing them to participate in proposal voting without restrictions.
- Governance Integration
- Delegators leveraging NFT-based delegation can vote on governance proposals identically to standard delegators.
- This ensures no distinction in governance rights between NFT and standard delegations, maintaining consistency across the system.
- Penalty Handling
- The module enforces penalty mechanisms that apply proportionally to NFT-based delegations.
- If a validator incurs penalties, the corresponding reduction in balance affects both standard delegations and NFT balances.
- This ensures that NFT-based delegations are subject to the same economic risks and responsibilities as traditional delegations.
Architecture and Implementation Details
-
Integration with CosmosSDK Staking Logic:
- The module seamlessly integrates NFT-based delegations into the existing CosmosSDK staking framework.
- It ensures compatibility with current staking operations, including delegation, undelegation, and redelegation workflows.
-
Custom NFT Representation:
- Each NFT encapsulates the locked tokens and is tracked within the staking system.
- Voting power is calculated based on the locked amount represented by the NFT, ensuring parity with standard token delegations.
-
Penalty Application:
- Penalties are directly applied to the NFT's balance when imposed on the associated validator.
- The module automatically adjusts the NFT representation to reflect any slashed or penalized amounts.
Mint & Distribution
The enhanced CosmosSDK mint and distribution modules extend the functionality of reward calculation for validators and delegators to incorporate support for non-fungible token (NFT) delegations. This update includes a reward bonus mechanism for NFT-based delegations while maintaining compatibility with the existing reward distribution processes.
Key Features and Functionality
- NFT-Based Rewards Calculation
- The module now calculates rewards for NFT-based delegations alongside standard delegations.
- Rewards are computed based on the voting power represented by the NFT, ensuring integration with the current distribution logic.
- Bonus for NFT Delegations
- NFT delegations receive a 20% bonus in reward calculation.
- This bonus is applied at the reward computation level by treating the NFT voting power as 20% greater than its actual value.
- The bonus incentivizes delegators to leverage NFTs for staking.
- Standard Rewards Behavior
- Rewards collected through NFT-based delegations function identically to rewards from standard delegations.
- Delegators can withdraw and manage NFT delegation rewards using the same processes as standard rewards, ensuring consistency and ease of use.
Architecture and Implementation Details
-
Integration with CosmosSDK Distribution Logic:
- The module incorporates additional logic for identifying and calculating rewards for NFT-based delegations.
- Voting power for NFTs is dynamically adjusted with the 20% bonus during reward computation, leaving the underlying staking mechanisms unaffected.
-
Reward Distribution:
- NFT rewards are processed and distributed through the same pipelines as standard rewards.
- Delegators retain the ability to withdraw rewards at their discretion, with no distinction between NFT-based and standard delegations.
-
Backward Compatibility:
- The module ensures that enhancements for NFT rewards do not interfere with standard delegation reward calculations.
- Validators and standard delegators experience no changes in functionality or behavior.
Changes in Protobuf
In the distribution module params, we define a new multiplier for rewards by NFT's staking. In our case this
field by default will be equal to 0.2000000...(20%).
message Params {
string nft_proposer_reward = 4 [
(cosmos_proto.scalar) = "cosmos.Dec",
(gogoproto.customtype) = "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/types.Dec",
(gogoproto.nullable) = false
];
}
In the staking module, we have added a field to store the count of staked tokens in raw representation (__not shares
__) (count of tokens sent from delegator to validator). We also extend the Delegation struct by adding a timestamp
field. This field stores the timestamp when the deposit has been updated.
message Delegation {
string amount = 4 [
(cosmos_proto.scalar) = "cosmos.Dec",
(gogoproto.customtype) = "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/types.Dec",
(gogoproto.nullable) = false
];
google.protobuf.Timestamp timestamp = 5 [(gogoproto.stdtime) = true, (gogoproto.nullable) = false] ;
}
In the mint module parameters, we have added fields that describe custom block rewards policy (linear distribution
with constant amount per block).
message Params {
option (gogoproto.goproto_stringer) = false;
// type of coin to mint
string mint_denom = 1;
// expected blocks per month
uint64 blocks_per_month = 2;
// block when no additional tokens will be minted
uint64 end_block = 3;
cosmos.base.v1beta1.Coin month_reward = 4
[(gogoproto.nullable) = false, (gogoproto.customtype) = "github.com/cosmos/cosmos-sdk/types.Coin"];
}
Updates of internal logic
Distribution module
-
calculateDelegationRewardsBetween This function calculates the rewards accrued by a delegation between two periods.
func (k Keeper) CalculateDelegationRewards(ctx sdk.Context, val stakingtypes.ValidatorI, del stakingtypes.DelegationI,
endingPeriod uint64) (rewards sdk.DecCoins) {
// Some unchanged code here
params := k.GetParams(ctx)
_, isNFTstake := k.nftKeeper.GetNFT(ctx, del.GetDelegatorAddr().String()) // Checks if this delegation is NFT
wrapStake := func(stake sdk.Dec) sdk.Dec { // Special wrapper to add additional 20% profit by NFT staking.
if isNFTstake {
return stake.Add(stake.Mul(params.NftProposerReward))
}
return stake
}
// Some unchanged code here
endingHeight := uint64(ctx.BlockHeight())
if endingHeight > startingHeight {
k.IterateValidatorSlashEventsBetween(ctx, del.GetValidatorAddr(), startingHeight, endingHeight,
func(height uint64, event types.ValidatorSlashEvent) (stop bool) {
if event.ValidatorPeriod > startingPeriod {
// Using wrapped stake amount
rewards = rewards.Add(k.calculateDelegationRewardsBetween(ctx, val, startingPeriod, endingPeriod, wrapStake(stake))...)
// Some unchanged code here
}
return false
},
)
}
// Some unchanged code here
// Calculate rewards for final period (also using wrapped stake amount)
rewards = rewards.Add(k.calculateDelegationRewardsBetween(ctx, val, startingPeriod, endingPeriod, wrapStake(stake))...)
return rewards
}The key update here is the anonymous function
wrapStake(sdk.Dec). ThewrapStakefunction checks whether the delegation is made by an NFT or not, and based on this, it updates the rewards accordingly. -
IncrementValidatorPeriod Increment validator period, returning the period just ended.
Since the total amount of rewards remains constant, but NFT delegators are entitled to receive a higher proportion of tokens, it is necessary to normalize the rewards.
func (k Keeper) IncrementValidatorPeriod(ctx sdk.Context, val stakingtypes.ValidatorI) uint64 {
// Some unchanged code here
params := k.GetParams(ctx)
// Iterating over all delegations and adding additional 20% profit for NFT delegations to take into account in the total stake amount divisor.
for _, del := range k.stakingKeeper.GetValidatorDelegations(ctx, val.GetOperator()) {
if _, found := k.nftKeeper.GetNFT(ctx, del.GetDelegatorAddr().String()); found {
tokens = tokens.Add(del.Amount.Add(del.Amount.Mul(params.NftProposerReward)))
continue
}
tokens = tokens.Add(del.Amount)
}
if tokens.IsZero() {
// Some unchanged code here
} else {
current = rewards.Rewards.QuoDecTruncate(tokens)
}
// Some unchanged code here
}The main update here is the following code segment, where all rewards are summed up in relation to the delegator's multiplier. All operations are adjusted based on the raw staked token amounts.
params := k.GetParams(ctx)
for _, del := range k.stakingKeeper.GetValidatorDelegations(ctx, val.GetOperator()) {
if _, found := k.nftKeeper.GetNFT(ctx, del.GetDelegatorAddr().String()); found {
tokens = tokens.Add(del.Amount.Add(del.Amount.Mul(params.NftProposerReward)))
continue
}
tokens = tokens.Add(del.Amount)
} -
FundCommunityPoolFromModule Transfers tokens from module account to community pool instead of burning them. It has been added to maintain the total number of tokens in the network.
func (k Keeper) FundCommunityPoolFromModule(ctx sdk.Context, amount sdk.Coins, senderModuleName string) error {
if err := k.bankKeeper.SendCoinsFromModuleToModule(ctx, senderModuleName, types.ModuleName, amount); err != nil {
err = sdkerrors.Wrap(err, "failed to fund community pool")
k.Logger(ctx).Error(err.Error())
return err
}
feePool := k.GetFeePool(ctx)
k.Logger(ctx).Info(fmt.Sprintf("amount of tokens in community pool before slashing is %s", feePool.CommunityPool.String()))
feePool.CommunityPool = feePool.CommunityPool.Add(sdk.NewDecCoinsFromCoins(amount...)...)
k.SetFeePool(ctx, feePool)
k.Logger(ctx).Info(fmt.Sprintf("amount of tokens in community pool after slashing is %s", feePool.CommunityPool.String()))
return nil
}It is used in
stakingmodule to update default slashing process.
Staking module
-
Delegate The
Delegateperforms a delegation, set/update everything necessary within the store. ThetokenSrcindicates the bond status of the incoming funds.func (k Keeper) Delegate(ctx sdk.Context, delAddr sdk.AccAddress, bondAmt math.Int, tokenSrc types.BondStatus,
validator types.Validator, subtractAccount bool) (newShares sdk.Dec, err error) {
// Some unchanged code here
delegation, found := k.GetDelegation(ctx, delAddr, validator.GetOperator())
if !found {
delegation = types.NewDelegation(delAddr, validator.GetOperator(), sdk.ZeroDec(), sdk.ZeroDec())
}
// Some unchanged code here
// Update delegation
delegation.Shares = delegation.Shares.Add(newShares)
delegation.Amount = delegation.Amount.Add(sdk.NewDecFromInt(bondAmt))
k.SetDelegation(ctx, delegation)
// Some unchanged code here
}Added setting of the delegation amount. In the first case, if no delegation found, it initializes the amount field with an empty value. Just before returning, we update the
delegation.Amountfield. -
Unbond The
Unbondmethod unbonds a particular delegation and perform associated store operations.func (k Keeper) Unbond(ctx sdk.Context, delAddr sdk.AccAddress, valAddr sdk.ValAddress, shares sdk.Dec) (amount math.Int, err error) {
// Some unchanged code here
validator, amount = k.RemoveValidatorTokensAndShares(ctx, validator, shares)
if validator.DelegatorShares.IsZero() && validator.IsUnbonded() {
// if not unbonded, we must instead remove validator in EndBlocker once it finishes its unbonding period
k.RemoveValidator(ctx, validator.GetOperator())
}
// Using the amount received from RemoveValidatorTokensAndShares before
delegation.Amount = delegation.Amount.Sub(sdk.NewDecFromInt(amount))
if delegation.Shares.IsZero() {
err = k.RemoveDelegation(ctx, delegation)
} else {
k.SetDelegation(ctx, delegation)
// call the after delegation modification hook
err = k.AfterDelegationModified(ctx, delegatorAddress, delegation.GetValidatorAddr())
}
if err != nil {
return amount, err
}
return amount, nil
}We moved the call to
RemoveValidatorTokensAndSharesearlier in the process. This is necessary to set the amount of tokens before updating the delegation. -
FundCommunityPoolFromModule hooks a
FundCommunityPoolFromModulefunction fromdistributionmodule and transfers tokens to community pool from module account.func (k Keeper) FundCommunityPoolFromModule(ctx sdk.Context, amount sdk.Coins, senderModuleName string) error {
if k.hooks != nil {
return k.hooks.FundCommunityPoolFromModule(ctx, amount, senderModuleName)
}
return nil
}It is used by
burnNotBondedTokensandburnBondedTokensas a replacing of default burning, preventing token burning when validator is slashed or jailed.
Mint module
-
SendFromAccumulator This function is used to sent tokens from validator pool to the accumulator module.
func (k Keeper) SendFromAccumulator(ctx sdk.Context, amount sdk.Coins) error {
err := k.accumulatorKeeper.DistributeToModule(ctx, accumulatortypes.ValidatorPoolName, amount, types.ModuleName)
if err != nil {
err = errors.Wrap(err, "failed to call accumulator module")
k.Logger(sdk.UnwrapSDKContext(ctx)).Error(err.Error())
return err
}
return nil
}This approach ensures that no new tokens will be created, and the amount of rewards for the validator is properly managed by the validator pool.
-
BeginBlocker The
BeginBlockermints new tokens for the previous block with custom policy.func BeginBlocker(ctx sdk.Context, k keeper.Keeper) {
defer telemetry.ModuleMeasureSince(types.ModuleName, time.Now(), telemetry.MetricKeyBeginBlocker)
params := k.GetParams(ctx)
// skip if all tokens already minted
if uint64(ctx.BlockHeight()) >= params.EndBlock {
return
}
monthReward := sdk.NewDecFromInt(params.MonthReward.Amount)
mintedAmount := monthReward.QuoInt(sdk.NewInt(int64(params.BlocksPerMonth)))
// mint coins, update supply
mintedCoin := sdk.NewCoin(params.MintDenom, mintedAmount.TruncateInt())
mintedCoins := sdk.NewCoins(mintedCoin)
err := k.SendFromAccumulator(ctx, mintedCoins)
if err != nil {
k.Logger(ctx).Error("failed to send tokens from accumulator")
return
}
// send the minted coins to the fee collector account
err = k.AddCollectedFees(ctx, mintedCoins)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
if mintedCoin.Amount.IsInt64() {
defer telemetry.ModuleSetGauge(types.ModuleName, float32(mintedCoin.Amount.Int64()), "minted_tokens")
}
ctx.EventManager().EmitEvent(
sdk.NewEvent(
types.EventTypeMint,
sdk.NewAttribute(sdk.AttributeKeyAmount, mintedCoin.Amount.String()),
),
)
}The following code snippet illustrates the process of minting tokens.
Gov module
- Tally This function iterates over the votes
and updates the tally of a proposal based on the voting power of the voters.
Add ability to vote taking into account NFT delegation. Also, to prevent possible malicious behaviour, this function ignores recent delegations.
func (keeper Keeper) Tally(ctx sdk.Context, proposal v1.Proposal) (passes bool, burnDeposits bool, tallyResults v1.TallyResult) {
// Some unchanged code here
votingParams := keeper.GetVotingParams(ctx)
// Some unchanged code here
keeper.IterateVotes(ctx, proposal.Id, func(vote v1.Vote) bool {
// Some unchanged code here
// get all nfts related for delegator
nfts, _, err := keeper.nftKeeper.GetAllNFTsByOwnerWithPagination(ctx, voter.String(), &query.PageRequest{Limit: query.MaxLimit})
if err != nil {
keeper.Logger(ctx).Error("failed to get all nfts for the validator ", err)
return false
}
// iterate over all delegator's nfts to calculate power
for _, nft := range nfts {
// iterate over all delegations from voter, deduct from any delegated-to validators
keeper.sk.IterateDelegations(ctx, sdk.MustAccAddressFromBech32(nft.Address), func(index int64, delegation stakingtypes.DelegationI) (stop bool) {
valAddrStr = delegation.GetValidatorAddr().String()
// validate that delegation is available to votes
if !delegation.GetTimestamp().Add(votingParams.LockingPeriod).Before(ctx.BlockTime()) {
keeper.Logger(ctx).Info(fmt.Sprintf("delegation %s is not yet unlocked", delegation.GetValidatorAddr().String()))
return false
}
if val, ok := currValidators[valAddrStr]; ok {
// There is no need to handle the special case that validator address equal to voter address.
// Because voter's voting power will tally again even if there will be deduction of voter's voting power from validator.
val.DelegatorDeductions = val.DelegatorDeductions.Add(delegation.GetShares())
currValidators[valAddrStr] = val
// delegation shares * bonded / total shares
votingPower := delegation.GetShares().MulInt(val.BondedTokens).Quo(val.DelegatorShares)
for _, option := range vote.Options {
weight, _ := sdk.NewDecFromStr(option.Weight)
subPower := votingPower.Mul(weight)
results[option.Option] = results[option.Option].Add(subPower)
}
totalVotingPower = totalVotingPower.Add(votingPower)
}
return false
})
}
// iterate over all delegations from voter, deduct from any delegated-to validators
keeper.sk.IterateDelegations(ctx, voter, func(index int64, delegation stakingtypes.DelegationI) (stop bool) {
valAddrStr = delegation.GetValidatorAddr().String()
// validate that delegation is available to vote
if !delegation.GetTimestamp().Add(votingParams.LockingPeriod).Before(ctx.BlockTime()) {
keeper.Logger(ctx).Info(fmt.Sprintf("delegation %s is not yet unlocked", delegation.GetValidatorAddr().String()))
return false
}
// Some unchanged code here
})
keeper.deleteVote(ctx, vote.ProposalId, voter)
return false
})