Overview
Bridgeless is designed as a robust and scalable solution for cross-chain interoperability. The architecture is composed of several key components that ensure the secure and efficient operation of the system. These components include both development-focused elements such as databases and message brokers, and architectural elements like validator nodes and threshold signature producers.
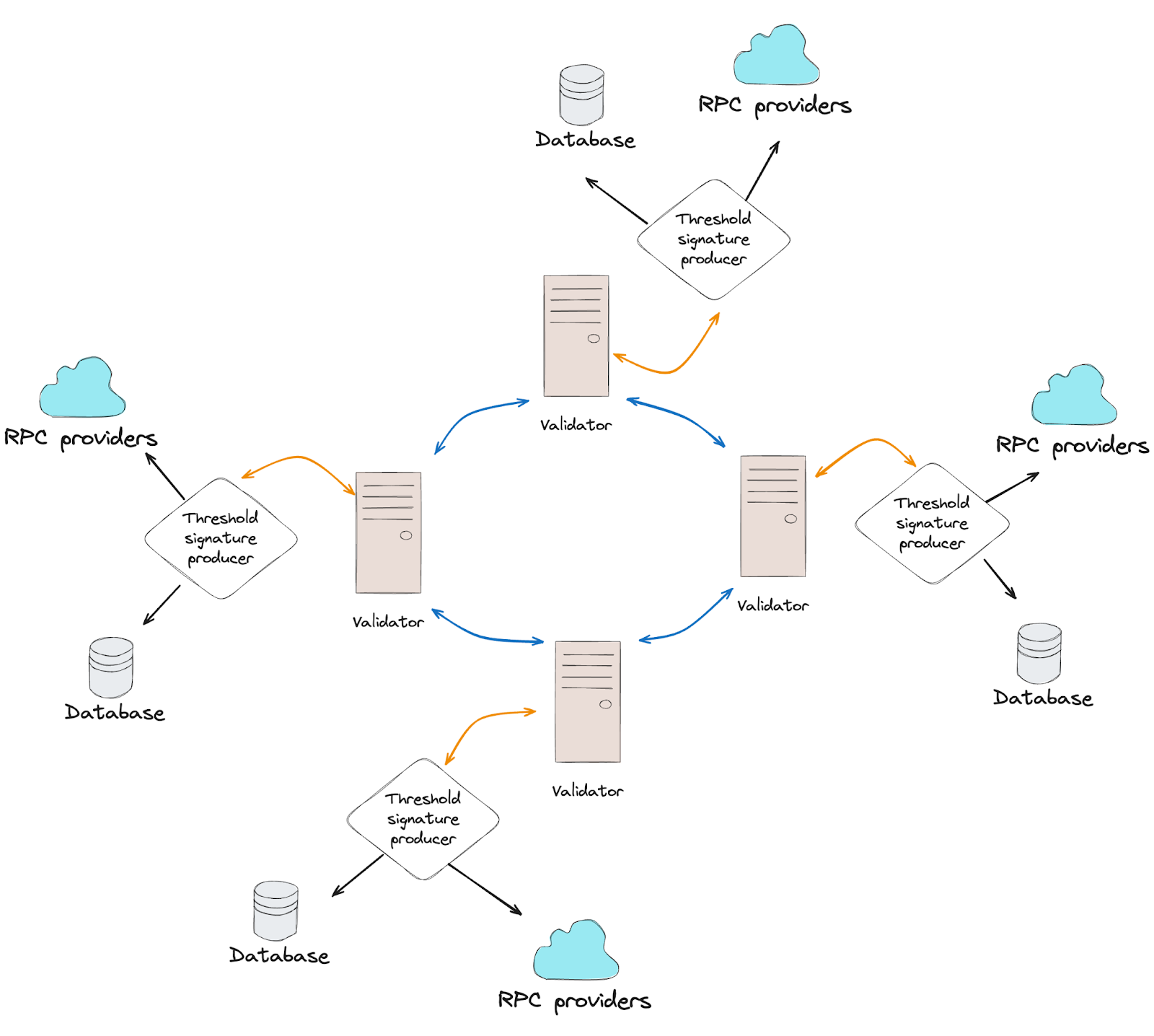
Components
Development-Focused Components
-
Databases and Message Brokers
- Databases store essential data related to token transfers, configurations, and other system operations.
- Message brokers facilitate reliable communication between system components.
-
RPC Providers
- Provide access to blockchain networks, enabling Bridgeless to interact with supported chains and fetch transaction data.
-
Threshold Signature Service
- Responsible for generating cryptographic signatures used in cross-chain operations.
-
Blockchain Core Service (Validator Node)
- Acts as the backbone of the system, ensuring data integrity and managing protocol-specific operations.
Architectural Components
-
Validator Nodes
- Operate in tandem with threshold signature producers.
- Utilize a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism to manage operations such as creating, updating, and deleting data as defined by the protocol.
- Support staking algorithms for native tokens and specialized NFTs.
- Implement custom token distribution schemes and maintain configuration data essential to bridge logic.
-
Threshold Signature Producers
- Establish connections with other threshold signature producers and validator nodes.
- Interact with RPC providers to retrieve transaction data.
- Handle user requests for deposit verification, withdrawal signing, and submission.
- Manage bridge liquidity migration and key regeneration in case of producer changes.
EVM Smart Contracts
EVM-compatible smart contracts are a vital part of Bridgeless, providing on-chain logic and security for operations. Key functionalities include:
-
Deposit Management
- Collect user deposits and emit events for transaction tracking.
-
Withdrawal Operations
- Verify ECDSA signatures to authorize withdrawals.
-
Key Management
- Support dynamic key changes by validating signatures from the current key.
- Optionally, provide a master key for administrative operations.
Interactions Between Components
-
Data Flow
- User actions, such as deposits, trigger smart contract events that are tracked by validator nodes.
- Validator nodes generate cryptographic proofs (witnesses) and interact with threshold signature producers to perform cross-chain operations.
-
Key Operations
- Validator nodes and signature producers work together to manage asset transfers and maintain system security.
- Database and message brokers ensure reliable data handling and communication between services.